Infrastructure as Code Testing: Van Chaos naar Gecontroleerde Deployments
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) heeft de manier waarop organisaties infrastructuur beheren fundamenteel veranderd. Toch zien we in de praktijk dat veel teams nog steeds worstelen met ongecontroleerde deployments, configuration drift en productie-incidenten die voorkomen hadden kunnen worden.
Dit blog biedt een praktische gids voor het implementeren van een robuuste IaC testing strategie, van basis validatie tot geavanceerde compliance monitoring.
Waarom IaC Testing Essentieel is
Moderne organisaties deployen infrastructuur meerdere keren per dag. Zonder adequate testing kunnen kleine fouten grote gevolgen hebben: downtime, security vulnerabilities, of compliance overtredingen. IaC testing biedt:
- Vroege detectie van problemen voordat ze productie bereiken
- Consistentie tussen environments (dev, staging, productie)
- Compliance en security door geautomatiseerde policy checks
- Confidence bij deployments door voorspelbare resultaten
De IaC Testing Strategie
Fase 1: Static Analysis - De Basis van Kwaliteit
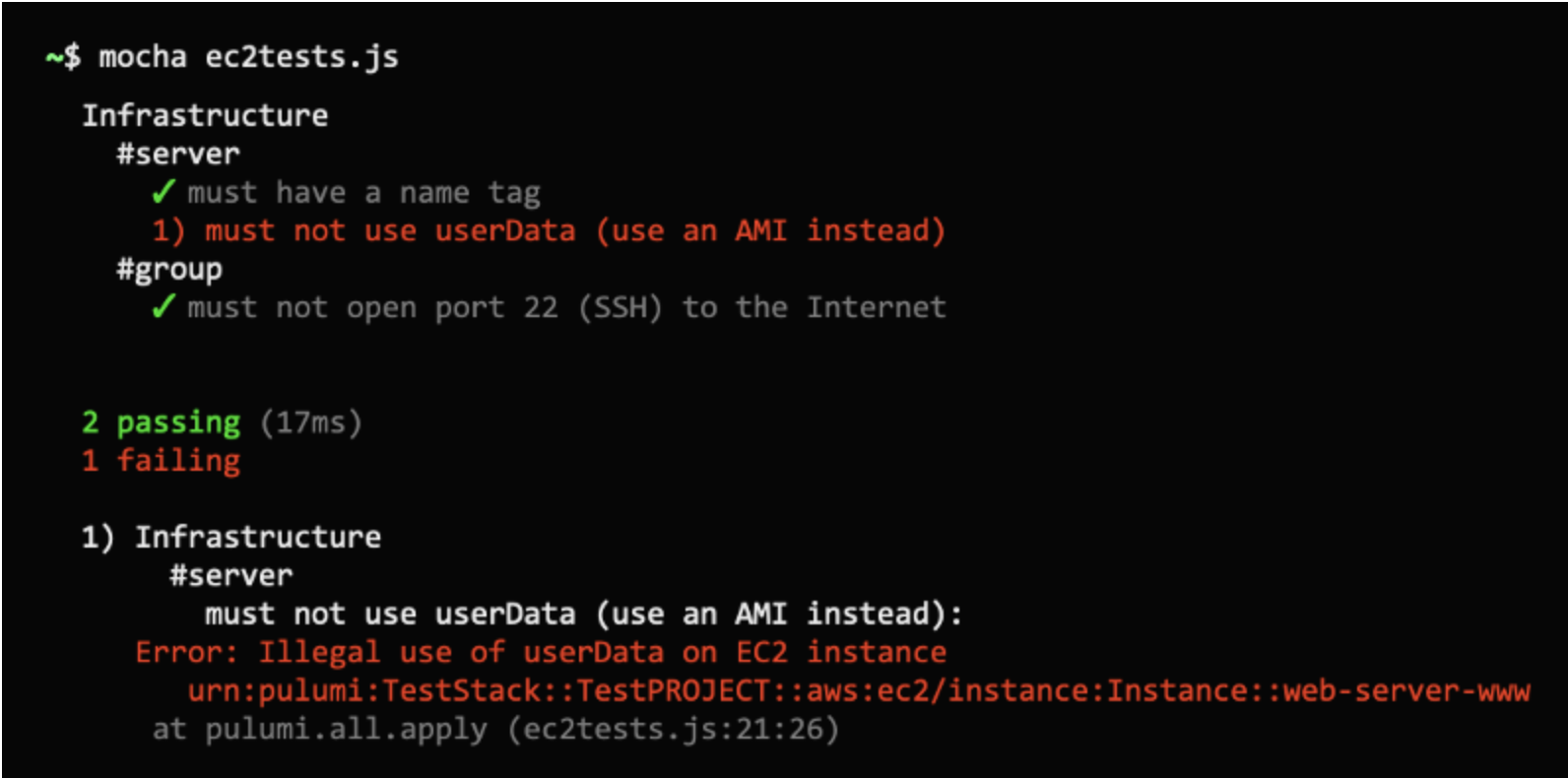
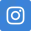
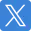
Static analysis vormt de foundation van elke IaC testing strategie. Deze tools analyseren code zonder deze uit te voeren en vangen syntaxfouten, security issues en best practice violations op.
Voor Terraform:
terraform validate # Syntax en configuratie validatie
tflint # Provider-specifieke linting
checkov -d . # Security en compliance scanning
tfsec . # Security-focused analysis
Voor AWS CloudFormation:
cfn-lint template.yaml # Template validatie
cfn-nag template.yaml # Security analysis
Voor Azure Bicep:
az bicep build --file main.bicep # Ingebouwde validatie
Deze tools integreren eenvoudig in bestaande development workflows en geven directe feedback tijdens het ontwikkelproces.
Fase 2: Plan Validation - “Wat Als” Scenario’s
Na static analysis volgt plan validation - het analyseren van voorgestelde infrastructuurwijzigingen zonder deze daadwerkelijk uit te voeren.
Terraform Plan Analysis:
terraform plan -detailed-exitcode -out=tfplan
terraform show -json tfplan > plan.json
Policy Testing met Conftest:
package terraform.security
deny[msg] {
resource := input.resource_changes[_]
resource.type == "aws_s3_bucket"
not resource.change.after.versioning[_].enabled
msg := "S3 buckets must have versioning enabled"
}
Compliance Testing met terraform-compliance:
Feature: Security Compliance
Scenario: S3 buckets must not be publicly accessible
Given I have AWS S3 Bucket defined
When it contains public_read_write_access
Then its value must be False
Deze aanpak stelt teams in staat om security en compliance policies af te dwingen voordat infrastructuur wordt gedeployed.
Fase 3: Lokaal Testen - Cost-Effectieve Validatie
Lokale testing tools maken het mogelijk om infrastructuur te testen zonder cloud kosten te maken tijdens development.
LocalStack voor AWS: LocalStack emuleert AWS services lokaal, ideaal voor development en CI/CD pipelines:
import boto3
def test_s3_bucket_lifecycle():
s3 = boto3.client('s3', endpoint_url='http://localhost:4566')
# Create bucket
s3.create_bucket(Bucket='test-bucket')
# Verify lifecycle configuration
response = s3.get_bucket_lifecycle_configuration(Bucket='test-bucket')
assert len(response['Rules']) > 0
Moto voor Python-based Testing:
from moto import mock_ec2
import boto3
@mock_ec2
def test_ec2_security_group():
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name='us-east-1')
# Test security group creation
response = ec2.create_security_group(
GroupName='test-sg',
Description='Test security group'
)
assert response['GroupId'].startswith('sg-')
Fase 4: Integration Testing - End-to-End Validatie
Integration testing valideert dat infrastructuurcomponenten correct samenwerken door daadwerkelijke resources te deployen in test environments.
Terratest Framework:
func TestWebServerCluster(t *testing.T) {
terraformOptions := &terraform.Options{
TerraformDir: "../examples/web-cluster",
Vars: map[string]interface{}{
"cluster_size": 3,
"instance_type": "t3.micro",
},
}
defer terraform.Destroy(t, terraformOptions)
terraform.InitAndApply(t, terraformOptions)
// Validate load balancer
url := terraform.Output(t, terraformOptions, "load_balancer_url")
http_helper.HttpGetWithRetry(t, url, nil, 200, "Hello World", 30, 5*time.Second)
// Validate auto-scaling
asgName := terraform.Output(t, terraformOptions, "asg_name")
asg := aws.GetAsgByName(t, asgName, "us-east-1")
assert.Equal(t, int64(3), *asg.DesiredCapacity)
}
AWSpec voor AWS Resource Validation:
describe ec2('web-server-1') do
it { should be_running }
it { should have_security_group('web-server-sg') }
its(:instance_type) { should eq 't3.micro' }
end
describe security_group('web-server-sg') do
it { should allow_inbound_tcp_port(80).from('0.0.0.0/0') }
it { should_not allow_inbound_tcp_port(22).from('0.0.0.0/0') }
end
Geavanceerde Testing Technieken
Configuration Drift Detection
Configuration drift - wanneer werkelijke infrastructuur afwijkt van de gedefinieerde code - is een veelvoorkomend probleem in productieomgevingen.
Geautomatiseerde Drift Detection:
#!/bin/bash
# Wekelijkse drift check
terraform plan -detailed-exitcode
case $? in
0) echo "No changes needed" ;;
1) echo "Error in terraform plan" && exit 1 ;;
2) echo "Infrastructure drift detected" && send_alert ;;
esac
AWS Config voor Continuous Monitoring:
{
"ConfigRuleName": "s3-bucket-ssl-requests-only",
"Source": {
"Owner": "AWS",
"SourceIdentifier": "S3_BUCKET_SSL_REQUESTS_ONLY"
}
}
Multi-Environment Consistency Testing
Consistentie tussen environments is cruciaal voor betrouwbare deployments:
def test_environment_consistency():
environments = ['dev', 'staging', 'prod']
configs = {}
for env in environments:
configs[env] = get_terraform_outputs(env)
# Verify consistent security group rules
base_rules = configs['dev']['security_group_rules']
for env in ['staging', 'prod']:
assert configs[env]['security_group_rules'] == base_rules
# Verify consistent instance families (size may differ)
base_family = configs['dev']['instance_type'].split('.')[0]
for env in ['staging', 'prod']:
env_family = configs[env]['instance_type'].split('.')[0]
assert env_family == base_family
Infrastructure Resilience Testing
Testing van failover scenarios en disaster recovery procedures:
func TestAutoScalingResilience(t *testing.T) {
// Get current instances
instanceIds := aws.GetEc2InstanceIdsByTag(t, awsRegion, "Environment", "test")
originalCount := len(instanceIds)
// Terminate random instance
aws.TerminateInstance(t, awsRegion, instanceIds[0])
// Verify auto-scaling group replaces instance
retry.DoWithRetry(t, "Instance replacement", 10, 30*time.Second, func() (string, error) {
currentInstances := aws.GetEc2InstanceIdsByTag(t, awsRegion, "Environment", "test")
if len(currentInstances) >= originalCount {
return "Instance replaced successfully", nil
}
return "", fmt.Errorf("Waiting for instance replacement")
})
}
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Een effectieve IaC testing strategie integreert alle testing fases in de CI/CD pipeline:
name: Infrastructure Pipeline
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
static-analysis:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Static Analysis
run: |
terraform validate
tflint --config=.tflint.hcl
checkov -d . --framework terraform
plan-validation:
needs: static-analysis
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Terraform Plan
run: |
terraform init
terraform plan -out=tfplan
terraform show -json tfplan > plan.json
- name: Policy Validation
run: conftest test --policy policy/ plan.json
integration-test:
needs: plan-validation
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
steps:
- name: Deploy Test Environment
run: terraform apply -auto-approve
- name: Run Integration Tests
run: go test -v ./tests/integration/...
- name: Cleanup
if: always()
run: terraform destroy -auto-approve
Tool Selectie per Platform
De keuze van testing tools hangt af van je IaC platform en specifieke requirements:
| Platform | Static Analysis | Security | Integration | Policy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terraform | TFLint, terraform validate | TFSec, Checkov | Terratest | Conftest/OPA |
| CloudFormation | cfn-lint | cfn-nag | AWSpec | AWS Config Rules |
| Bicep | Bicep linter | PSRule for Azure | Pester | Azure Policy |
| CDK | Built-in validation | cdk-nag | Jest/Testing Library | Custom assertions |
Best Practices voor IaC Testing
1. Implementeer de Testing Pyramid
- 70% Unit tests: Snelle, lokale validatie
- 20% Integration tests: Component interacties
- 10% End-to-end tests: Volledige workflows
2. Shift-Left Testing
- Pre-commit hooks voor immediate feedback
- IDE integraties voor real-time validation
- Developer workstation testing tools
3. Test Data Management
- Gebruik realistische test data
- Implementeer automatische cleanup procedures
- Tag test resources voor cost tracking
4. Monitoring en Feedback
- Monitor test execution times
- Track test coverage metrics
- Implement alerting voor failing tests
ROI van IaC Testing
Organisaties die comprehensive IaC testing implementeren rapporteren:
- 60-80% reductie in infrastructure-gerelateerde incidents
- 50% snellere mean time to recovery (MTTR)
- 40% verhoogde deployment frequency
- Significante kostenbesparing door vroege detectie van problemen
Conclusie
IaC testing is geen optie meer - het is een noodzaak voor moderne infrastructuur management. Door een gestructureerde aanpak te volgen, van static analysis tot end-to-end testing, kunnen organisaties de betrouwbaarheid en security van hun infrastructuur significant verbeteren.
Begin met de basics: static analysis en plan validation. Bouw geleidelijk uit naar integration testing en geavanceerde technieken. De investering in testing infrastructure pays off door reduced incidents, faster debugging, en increased deployment confidence.
De tools en technieken bestaan al. Het enige wat nodig is, is de commitment om infrastructure met dezelfde zorgvuldigheid te behandelen als application code.
Voor meer informatie over specifieke tools en implementatie details, raadpleeg de officiële documentatie of neem contact op via LinkedIn.